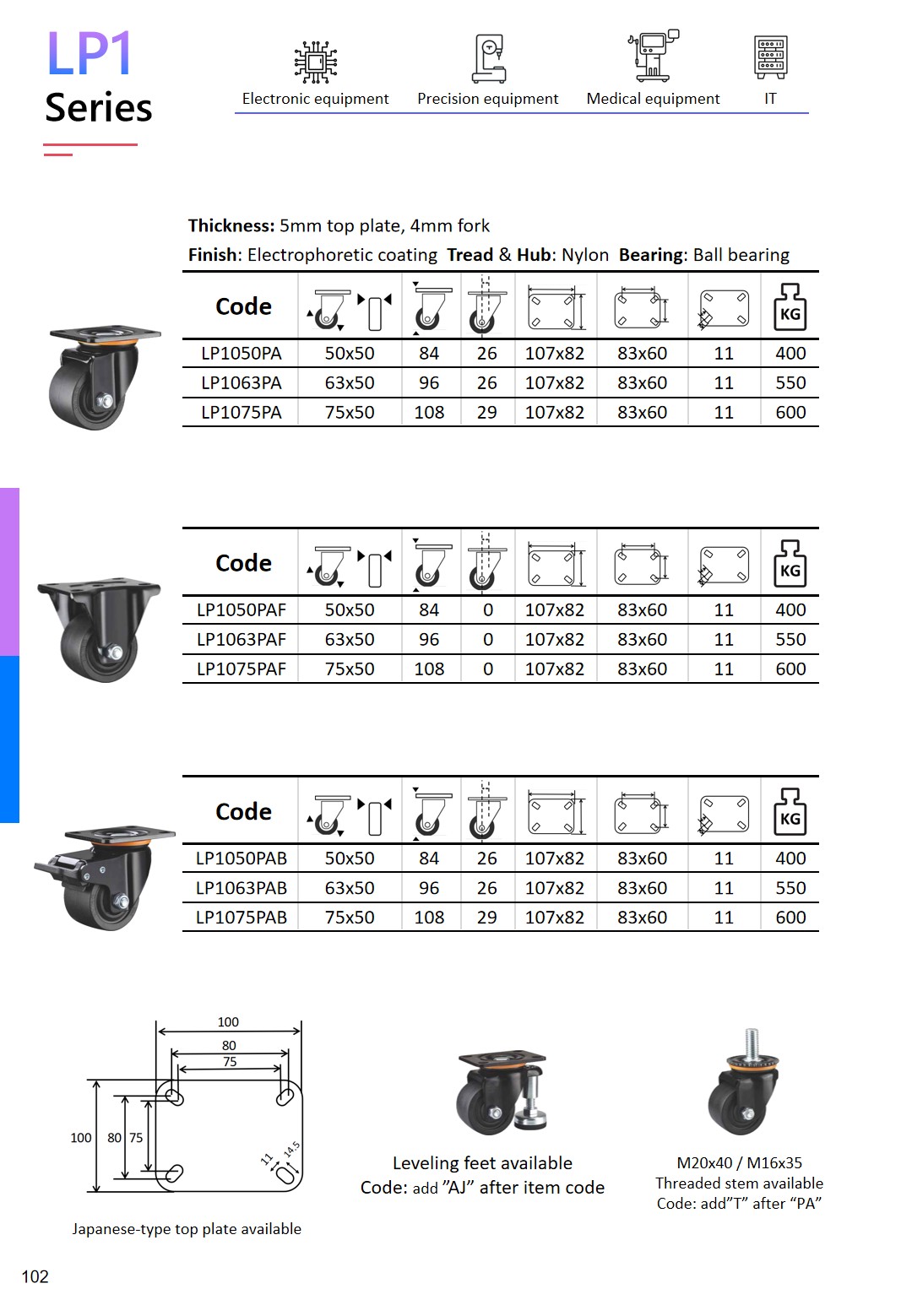
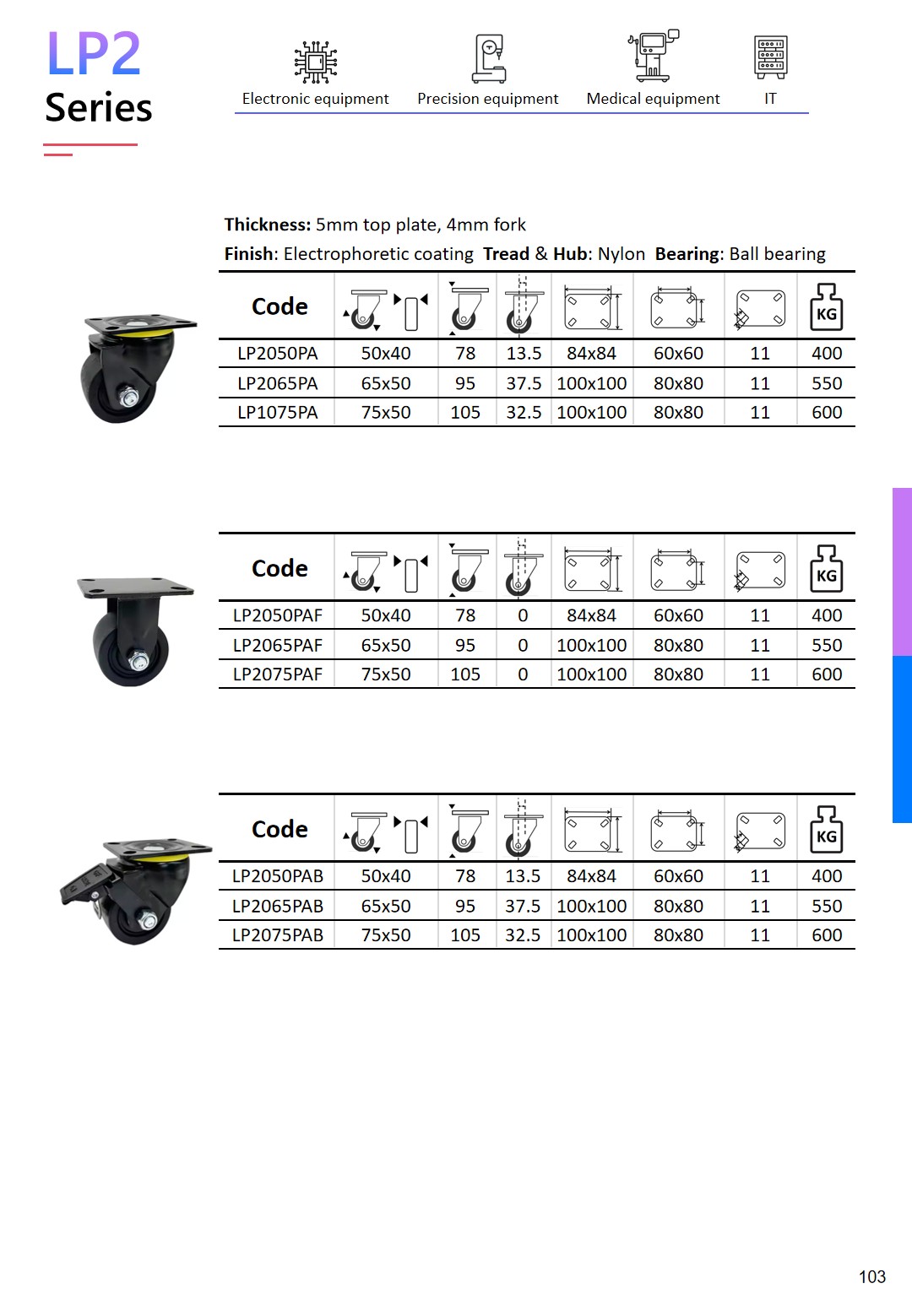
expert casters for equipment that requires minimum caster assembly height.
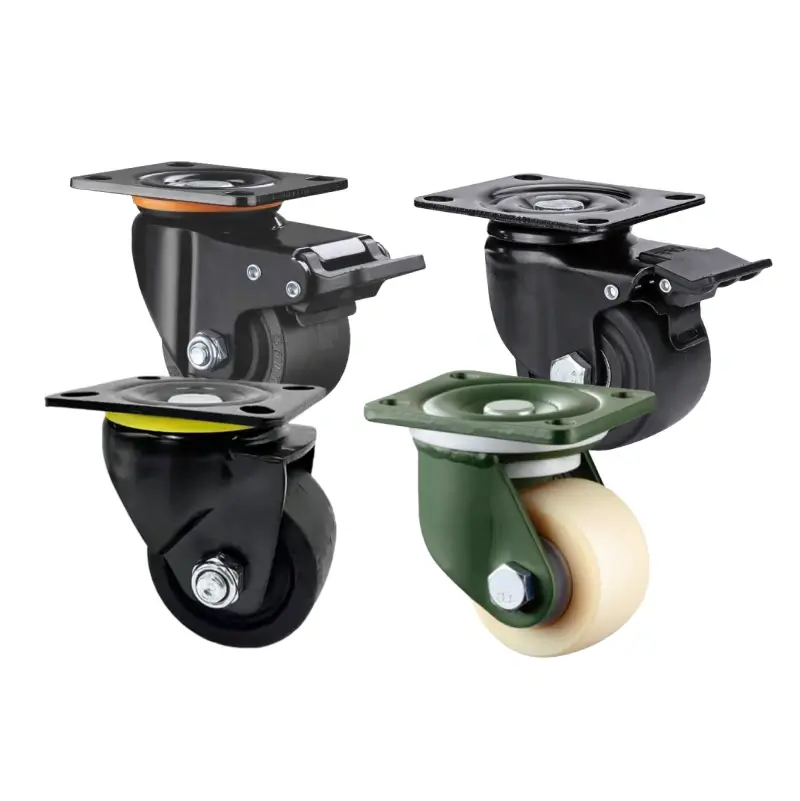


Low-profile casters are compact wheel assemblies that minimize mounting height while preserving mobility and load capacity. They’re used where clearance is tight—under server racks, vending machines, medical carts, and cabinetry—to lower overall height, stabilize the center of gravity, and move equipment in limited space.
The total height from floor to mounting surface is lower than standard casters, enabling clearance under low furniture or equipment.
Often features a wider wheel contact area to maintain stability despite the reduced height.
Some models use reinforced frames or larger contact patches to support heavy loads while keeping the profile low.
Uses PA6 or reinforced Nylon wheels and E-coated brackets, capable of withstanding up to 500 hours of salt spray corrosion testing.
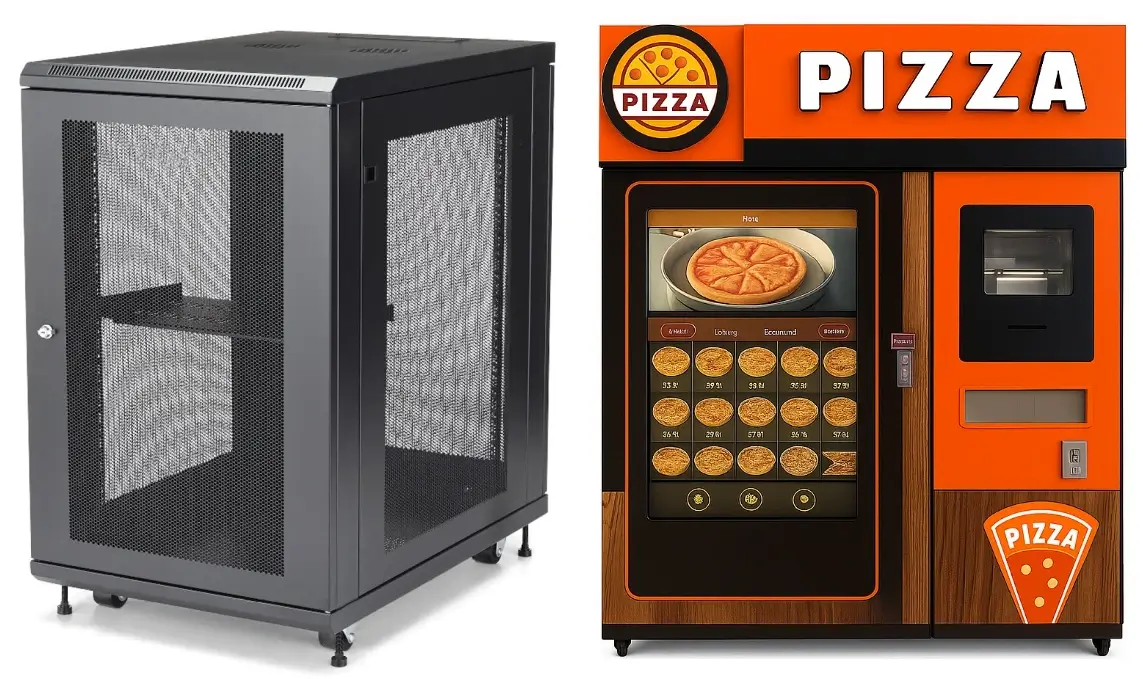

Vending machine, server racks, data-center racks, 19 inch racks, retail fixtures, electronic enclosures, mobile workstations, etc.
Our range helps you reduce overall height, protect sensitive instruments, and speed changeovers


24~72 hours salt spray test passed

500 hours salt spray test passed

1,000 hours salt spray test passed
50mm~100mm
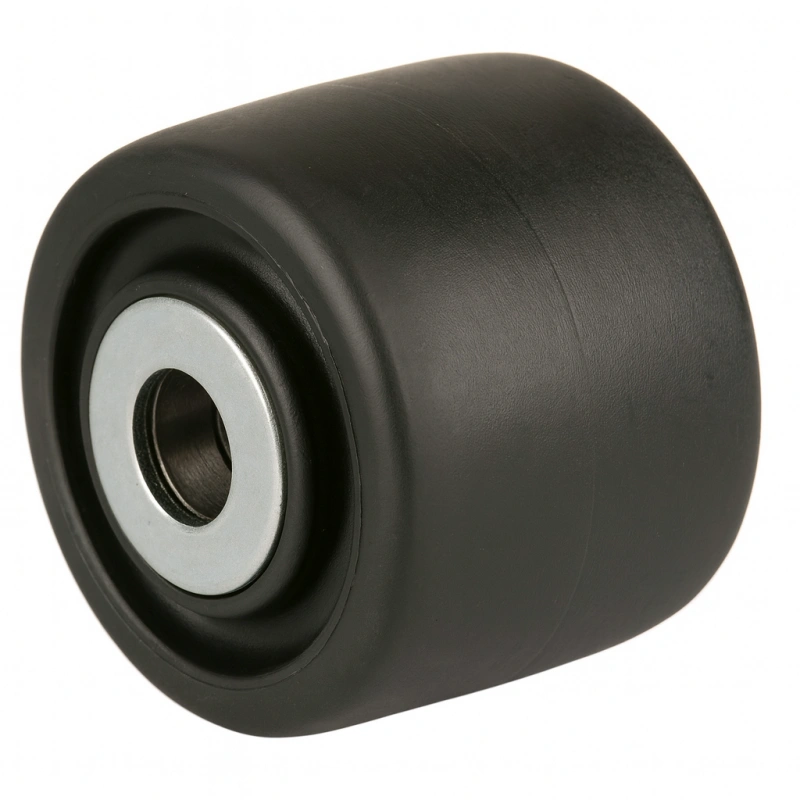

Bearing: Double ball bearings

Bearing: Double ball bearings

Up to 600KGs

| Criteria | Leveling casters | Low-profile casters |
|---|---|---|
| Core purpose |
Designed to create a stable, level base on uneven floors or when precise leveling is required under load. They combine mobility with a leveling mechanism to compensate for floor irregularities. |
Designed to minimize overall height while preserving mobility and load-bearing capacity. They emphasize space efficiency and clearance rather than dynamic leveling. |
| When to use |
Use when equipment must operate level in place (e.g., machinery bases, workstations, hospital beds, or heavy carts that must be leveled during operation). |
Use when clearance is limited (under cabinets, server racks, display cases, or slim furniture) and mobility is needed without compromising height constraints. |
| Mechanism and components |
Incorporate a leveling element (foot pad, screw jack, lever-operated pad, or auto-leveling actuator) that engages to raise or stabilize the wheel/contact surface. Often include a locking or braking function that works in tandem with leveling. |
Feature a reduced overall mounting height, often with a broader wheel footprint or reinforced frames to maintain stability at a lower height. They may be rigid (no swivel) or swivel with brakes, but typically do not include an active leveling mechanism. |
| Load and stability behavior |
Prioritize static and dynamic stability at a level state; performance is judged by leveling accuracy, repeatability, and how well the load remains level under movement or varying loads. |
Prioritize maximizing load capacity relative to their compact height, stability during movement, and floor interface, with emphasis on minimizing interference with surrounding spaces. |
Designing and manufacturing custom casters for an OEM project involves several stages, we follow a detailed step-by-step process to ensure that your project runs smoothly and without any problems
Define requirements: Understand the customer’s specific needs and requirements. Consider special attachments, test standards, and industry standards. Give suggestions to improve the caster performance if the customer wants to eliminate the failure issues from their existing casters.
Material selection: Select appropriate wheel materials for the casters based on factors like load capacity, environmental conditions, and durability requirements.
Technical Drawings: Make detailed 2D/3D technical drawings of the caster based on the customer’s requirements or samples.
Prototyping: Develop prototypes to test the functionality and performance of the casters. It can be a 3D printing model or a small batch for initial testing.
Tooling and Equipment Setup: On the basis of the finalized design, set up and adjust the necessary tooling and equipment for mass production.
Production of Components: Manufacture individual caster components such as wheels and frames, according to technical specifications in confirmed drawings.
Surface Treatment: Apply surface treatments to enhance the aesthetics, corrosion resistance, hardness, or other functional aspects of the casters.
Assembly: Assemble the casters, making sure that each unit meets the design specifications and quality standards.
Load Testing: Test the casters according to the dynamic load test standard, such as EN12532, or conform to the test requirements of the customer. To ensure that the casters can handle the specified weight capacities without failure.
Durability Testing: Test the casters for durability under various conditions, such as different floor surfaces and temperature extremes, according to the customer’s demand.
Quality Control Checks: Implement ISO9001 quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process. Identify and correct any defects.
Packaging: Develop packaging solutions that protect the casters during transportation and storage.
Shipping Logistics: Plan and coordinate the logistics for shipping the casters to the client, and confirm the paperwork details with the customer, such as invoice and packing list, bill of lading, Certificate of Original, Form E, etc.
Customer Support: Provide ongoing support to address any queries, concerns, or further needs that the client may have after receiving the casters.
A low‑profile caster is a wheel assembly with a very low overall height designed to bring equipment or furniture closer to the ground while still carrying a heavy load. These casters lower the centre of gravity without sacrificing durability.
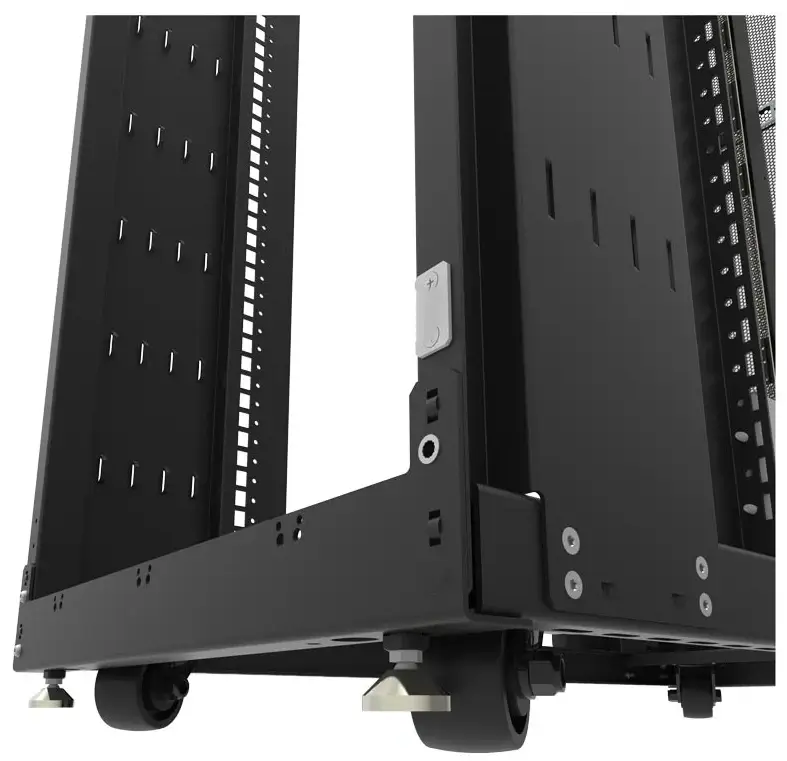

Heavy‑duty low‑profile casters are used to move industrial machinery, automation lines, medical equipment and warehouse logistics systems. They also appear under printing presses, portable tool cabinets, lab apparatus and CNC devices for confined industrial spaces and in business machines, technology racks, vending machines and server cabinets where clearance is limited.
Common sizes range from 2″ to 5″ diameters with corresponding load capacities: 2″ casters handle ~50‑150 kg, 3″ handle 150‑300 kg, 4″ handle 300‑500 kg and 5″ casters handle 500‑1 000 kg or more
Key benefits include high stability (low centre of gravity reduces tipping risk), high load capacity for their size, flexible movement in narrow spaces and reduced equipment height
Yes. Their smaller wheels may struggle on uneven surfaces or over obstacles, the range of wheel sizes is limited and they may cost more than standard casters
For height‑restricted applications, lower casters are usually better because they maintain stability; taller casters raise the centre of gravity and increase tipping risk.
Selection should consider load capacity, wheel size, floor conditions, environment and required mobility.
For heavy machinery, choose reinforced brackets and high‑capacity wheels; for sensitive floors, select non‑marking materials like glass‑filled Nylon. Contact us to get matching caster height to clearance requirements and using leveling models for precision tasks.
Yes we offer OEM/ODM services allowing buyers to customise wheel materials, bracket finishes, mounting types, packaging and even logo. Contact us tailored solutions for load, installation and design requirements
we are just one click away
*We respect your privacy and all your information are protected.