For aluminum scaffolding, mobile scaffold, scaffold towers, cuplock scaffold, ringrock scaffold, etc
Hello! Welcome to Wheelsway. This page introduces our scaffolding casters, covering definitions, common applications, and technical specifications. If you’re looking for more details or have a specific project in mind, you’re welcome to reach out and start a conversation. Let’s talk!
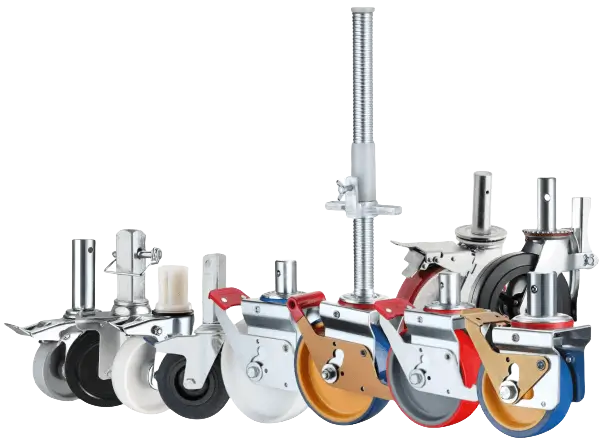


A scaffolding caster is a heavy‑duty wheel assembly designed specifically to convert a fixed scaffold into a safe, mobile structure. Unlike standard plate casters, scaffolding casters use a stem that inserts into pre‑drilled holes at the base of a scaffold frame. Once installed, they let workers roll the entire scaffold to different areas on a jobsite, avoiding repeated disassembly and reassembly.
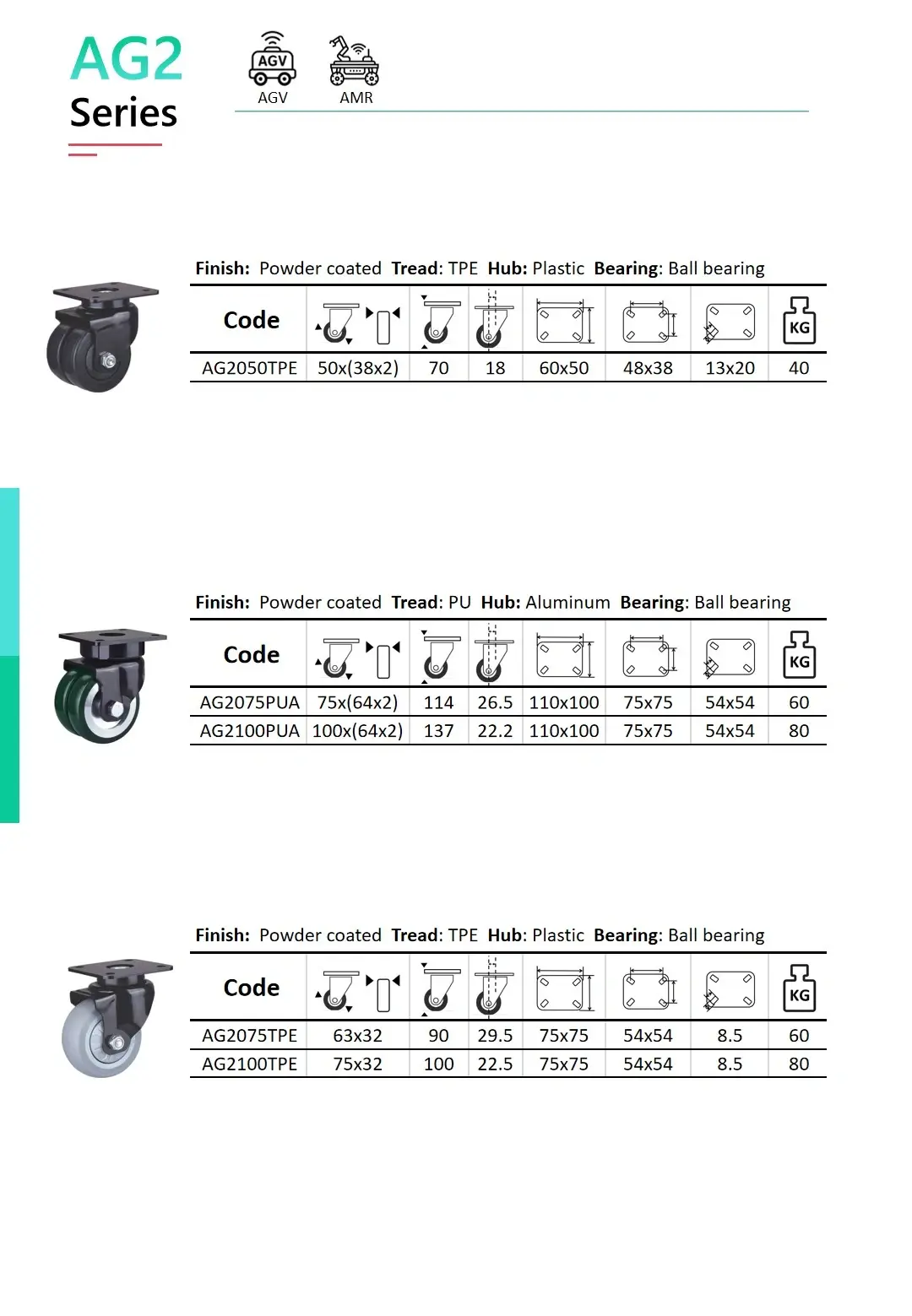
Enable precise and stable autonomous movement, and Improve navigation and path-tracking accuracy.
Support continuous 24/7 industrial operation
Reduce rolling resistance, power consumption, and wear on industrial floors.
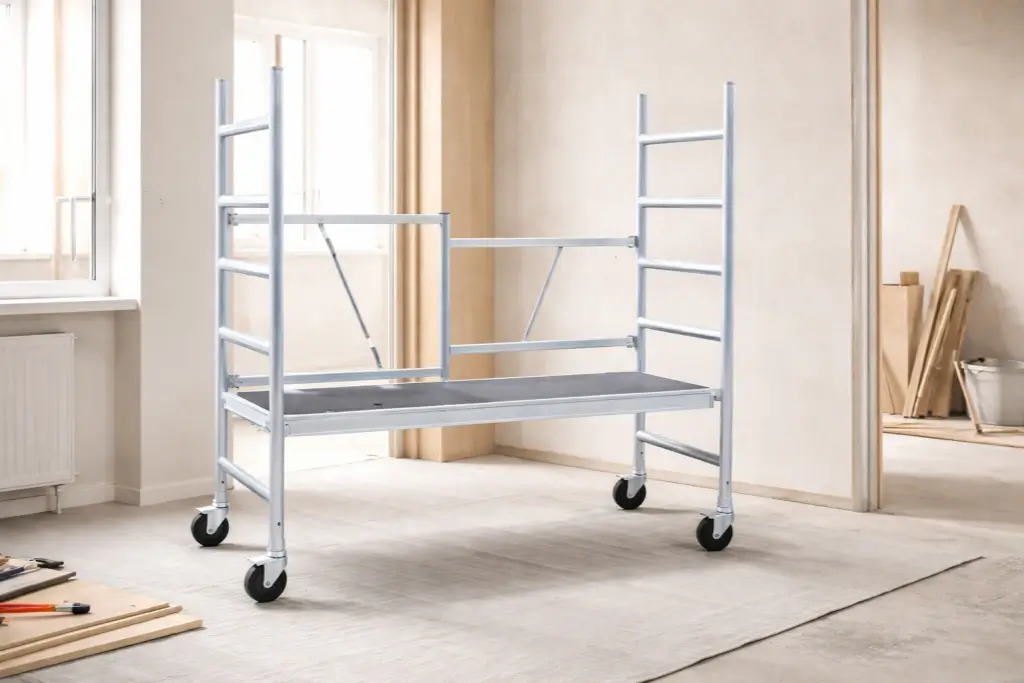




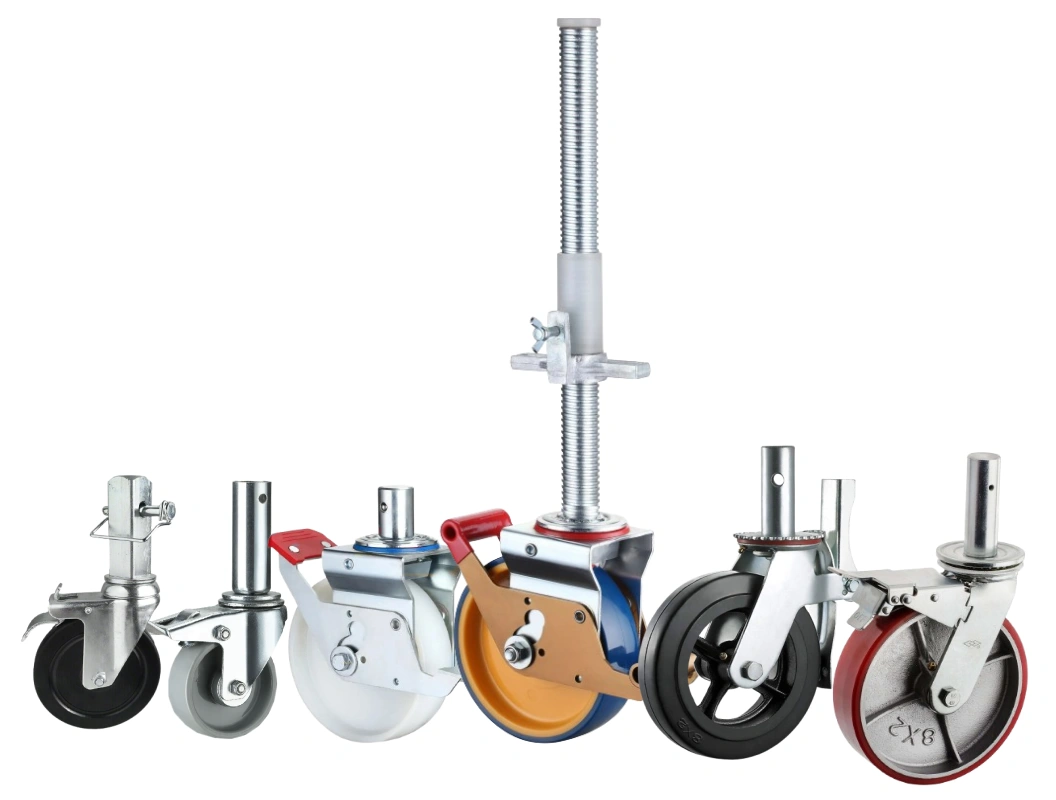
A scaffolding caster is a heavy‑duty wheel assembly designed specifically to convert a fixed scaffold into a safe, mobile structure. Unlike standard plate casters, scaffolding casters use a stem that inserts into pre‑drilled holes at the base of a scaffold frame. Once installed, they let workers roll the entire scaffold to different areas on a jobsite, avoiding repeated disassembly and reassembly.



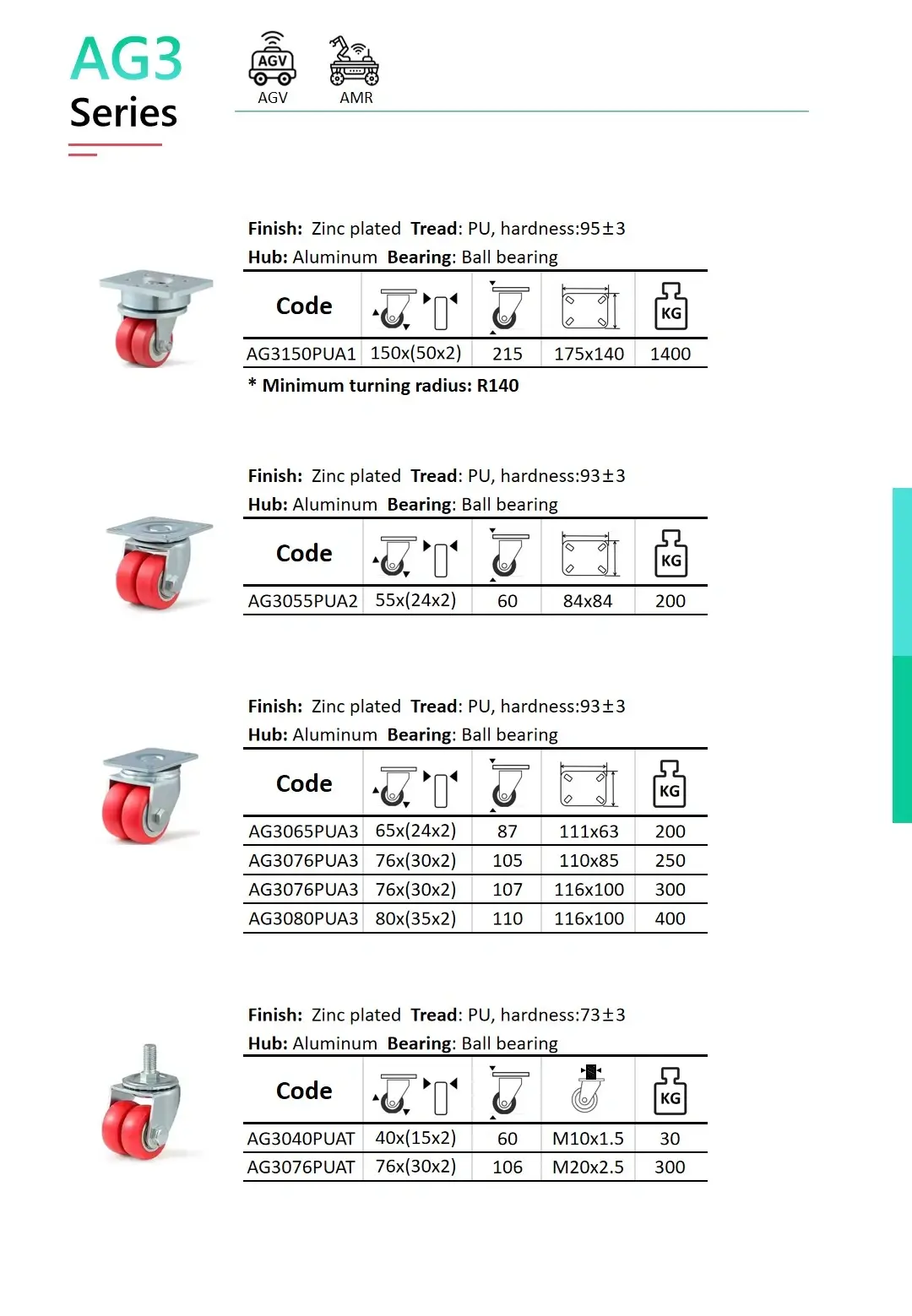
24~72 hours salt spray test passed

500 hours salt spray test passed
40mm~150mm

Bearing: Double ball bearings

Bearing options: Roller bearing / Double ball bearings
Up to 1,400KGs



24~72 hours salt spray test passed

500 hours salt spray test passed
40mm~150mm

Bearing: Double ball bearings

Bearing options: Roller bearing / Double ball bearings
Up to 1,400KGs


Casters for all kinds of scaffolds
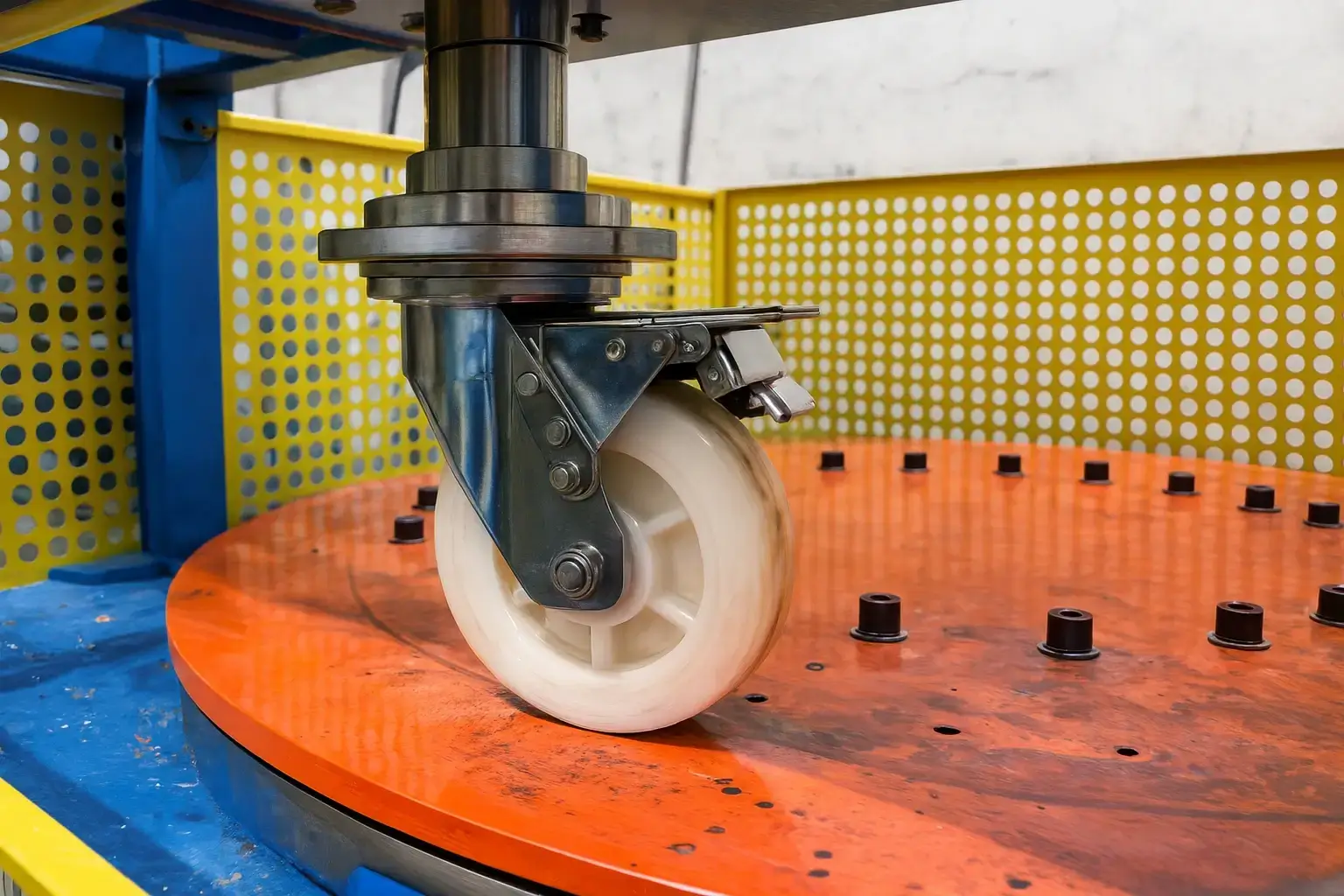

EN 12533 is the standard for heavy-duty castors and wheels used in applications where travel speeds are higher than walking pace – specifically over 1.1 m/s (4 km/h) and up to 4.4 m/s (16 km/h). It covers castors (including any accessories like brakes) designed for mechanical or power-driven applications in this speed range. This means equipment that is either powered or towed by a vehicle, moving at moderate running speeds. EN 12533 represents the upper end of caster usage, where significant dynamic forces occur due to higher speeds. The standard sets out technical specs, dimensions, and required tests to ensure safety and performance at these speeds. Importantly, EN 12533 excludes certain wheel types: pneumatic-tyred wheels (inflatable wheels) and dedicated drive wheels are not covered, as those may fall under other vehicle or machinery standards.
EN 12533 is the standard for heavy-duty castors and wheels used in applications where travel speeds are higher than walking pace – specifically over 1.1 m/s (4 km/h) and up to 4.4 m/s (16 km/h). It covers castors (including any accessories like brakes) designed for mechanical or power-driven applications in this speed range. This means equipment that is either powered or towed by a vehicle, moving at moderate running speeds. EN 12533 represents the upper end of caster usage, where significant dynamic forces occur due to higher speeds. The standard sets out technical specs, dimensions, and required tests to ensure safety and performance at these speeds. Importantly, EN 12533 excludes certain wheel types: pneumatic-tyred wheels (inflatable wheels) and dedicated drive wheels are not covered, as those may fall under other vehicle or machinery standards.

这是示例文本,单击 “编辑” 按钮更改此文本。
Designing and manufacturing custom casters for an OEM project involves several stages, we follow a detailed step-by-step process to ensure that your project runs smoothly and without any problems
Define requirements: Understand the customer’s specific needs and requirements. Consider special attachments, test standards, and industry standards. Give suggestions to improve the caster performance if the customer wants to eliminate the failure issues from their existing casters.
Material selection: Select appropriate wheel materials for the casters based on factors like load capacity, environmental conditions, and durability requirements.
Technical Drawings: Make detailed 2D/3D technical drawings of the caster based on the customer’s requirements or samples.
Prototyping: Develop prototypes to test the functionality and performance of the casters. It can be a 3D printing model or a small batch for initial testing.
Tooling and Equipment Setup: On the basis of the finalized design, set up and adjust the necessary tooling and equipment for mass production.
Production of Components: Manufacture individual caster components such as wheels and frames, according to technical specifications in confirmed drawings.
Surface Treatment: Apply surface treatments to enhance the aesthetics, corrosion resistance, hardness, or other functional aspects of the casters.
Assembly: Assemble the casters, making sure that each unit meets the design specifications and quality standards.
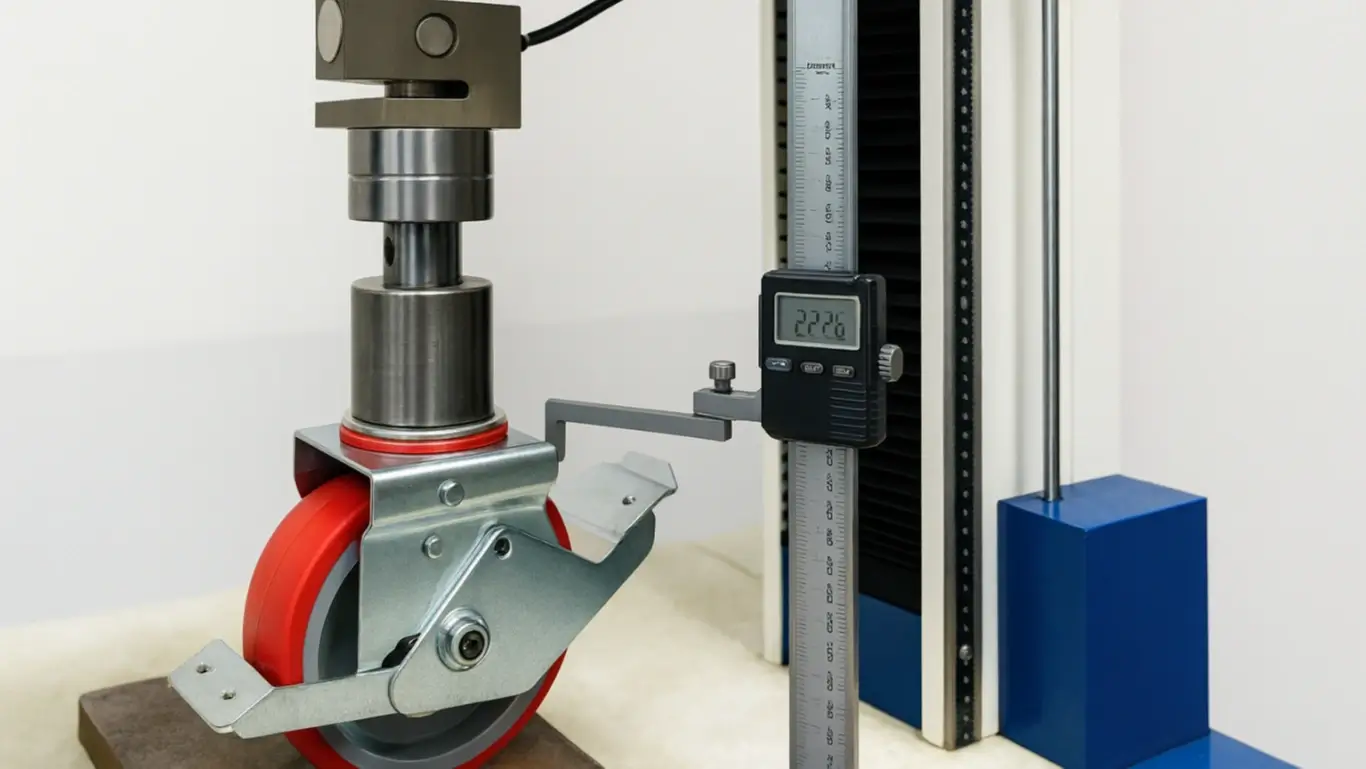
Load Testing: Test the casters according to the dynamic load test standard, such as EN12532, or conform to the test requirements of the customer. To ensure that the casters can handle the specified weight capacities without failure.
Durability Testing: Test the casters for durability under various conditions, such as different floor surfaces and temperature extremes, according to the customer’s demand.
Quality Control Checks: Implement ISO9001 quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process. Identify and correct any defects.
Packaging: Develop packaging solutions that protect the casters during transportation and storage.
Shipping Logistics: Plan and coordinate the logistics for shipping the casters to the client, and confirm the paperwork details with the customer, such as invoice and packing list, bill of lading, Certificate of Original, Form E, etc.
Customer Support: Provide ongoing support to address any queries, concerns, or further needs that the client may have after receiving the casters.
Unlike regular industrial casters, AGV casters are used for high-frequency automated motion, precise steering control, and consistent load distribution in robotics and automation environments. Standard industrial casters are not designed for continuous robotic use, which can lead to premature wear, navigation errors, and reduced system reliability.
Common AGV caster wheel materials include:
Polyurethane (PU) AGV wheels: Non-marking, durable, low rolling resistance
Rubber AGV wheels: Shock-absorbing, quieter operation
Nylon / engineering plastic AGV wheels: High load capacity, low friction
Material selection depends on load, speed, floor condition, and whether the AGV operates in cleanroom or industrial environments.
To choose the right AGV caster wheel, consider:
Required AGV caster load capacity per wheel
Wheel diameter and width to reduce rolling resistance
Wheel material based on floor surface and noise requirements
Mounting height and compatibility with AGV chassis design
These factors directly affect navigation accuracy, energy consumption, and wheel lifespan.
AGV casters should be rated above the AGV’s maximum load capacity, including payload and dynamic forces during acceleration and turning. Selecting Heavy-duty AGV casters with sufficient safety margin improves durability, reduces maintenance frequency, and supports long-term automated operation.
Different AGV wheel materials influence performance in specific ways:
Polyurethane AGV wheels reduce rolling resistance and protect floors
Rubber AGV wheels improve vibration damping and noise control
Nylon AGV wheels offer high strength but transmit more vibration
Material choice affects energy efficiency, floor wear, noise levels, and AGV navigation stability.
Yes. AGV caster maintenance is critical for reliable automation. Regular inspections should include:
Wheel tread wear
Bearing condition and lubrication
Swivel rotation accuracy
Proper maintenance reduces downtime and extends the service life of AGV caster wheels used in continuous operations.
Replacing AGV-specific casters with standard industrial casters is not recommended. Standard casters are not designed for continuous automated guidance, precision tracking, or robotic load patterns, which can lead to increased wear, navigation errors, and system instability.
Common AGV caster issues include:
Premature wear from incorrect wheel material
Reduced traction on smooth or contaminated floors
Overloading due to improper caster selection
Using proper AGV caster wheels helps mitigate these problems and ensures stable movement.
AGV casters are widely used in:
These industries require industrial automation caster wheels that deliver precision, durability, and continuous operation.
we are just one click away
*We respect your privacy and all your information are protected.