Managing a large-scale industrial operation? Then you know that choosing the wrong heavy-duty casters can lead to costly downtime and safety risks. I’ve worked with manufacturing plants and distribution centers worldwide, and I’ve seen how the right caster choice can dramatically impact operational efficiency and bottom-line results.
Quick Answer
Heavy-duty casters are industrial-grade wheel systems designed for loads exceeding 1,000 pounds per caster, with high-capacity models supporting 20,000+ pounds.
Selection criteria should prioritize:
- dynamic load rating (actual load capacity during movement)
- wheel material compatibility with floor surfaces
- operating temperature range (for example: -45°F to 180°F)
- turning radius requirements, and specific safety features like positive-lock braking systems.
Read on to discover the exact specifications you need for your industrial application, including detailed load calculations, material compatibility charts, and ROI-focused recommendations. Whether you’re outfitting an entire warehouse or upgrading your material handling equipment, this guide will help you make a data-driven decision.
What Are Heavy-Duty Casters?
Let’s start with the basics – but don’t worry, I won’t bore you with dictionary definitions. Heavy-duty casters are essentially industrial-strength wheel systems engineered specifically for demanding environments where standard casters just won’t cut it. Think of them as the heavyweight champions of the material handling world.
These aren’t your everyday shopping cart wheels. Heavy-duty casters are precision-engineered components designed to handle extreme weights while providing smooth movement and durability. They’re built with reinforced mounting plates, high-grade bearings, and specially formulated wheel materials that can stand up to punishing industrial conditions.
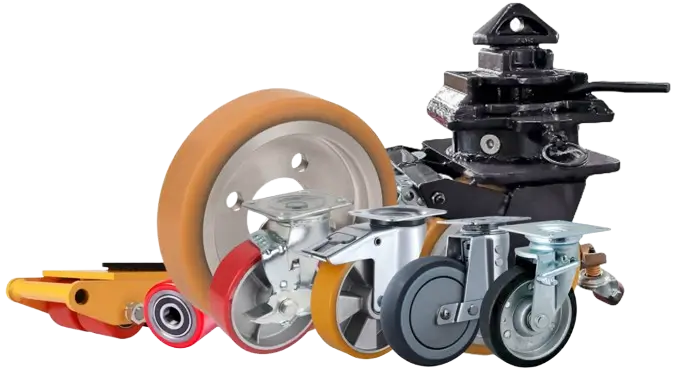
The Role of Casters in Industrial and Storage Applications
Here’s something most people don’t realize: your entire operation’s efficiency often hinges on these seemingly simple components. In modern industrial settings, heavy-duty casters are the unsung heroes that keep everything moving – literally.
Think about it. Your material handling equipment, storage systems, assembly line components, and maintenance platforms all rely on casters to function. They’re not just moving parts, they’re critical workflow enablers that can:
- Support massive loads while maintaining maneuverability
- Reduce worker strain and prevent workplace injuries
- Protect your expensive flooring from damage
- Maintain stability in dynamic environments
- Enable flexible space utilization in your facility
Benefits of Choosing the Right Casters
Safety
Because safety isn’t something to mess around with in industrial settings, so proper caster selection directly impacts workplace safety in several ways:
- Prevents tip-overs by ensuring adequate load support
- Reduces push/pull forces to prevent worker strain
- Provides reliable braking when needed
- Maintains stability during movement
Ergonomics
Here’s something your workers will thank you for: good ergonomics can dramatically reduce fatigue and increase productivity. The right casters can:
- Minimize the force needed to start movement (starting resistance)
- Reduce the effort required to keep loads in motion (rolling resistance)
- Allow for easier directional changes
- Help prevent repetitive strain injuries
Efficiency and Protection
From a business perspective, proper caster selection impacts your bottom line. Here’s how:
- Extends equipment lifespan by ensuring proper load distribution
- Protects floor surfaces from damage
- Reduces maintenance costs through better durability
- Improves operational speed and efficiency
- Minimizes downtime due to equipment failure
Step-by-Step Guide to Selecting the Best Caster
1. Choose the Heavy-Duty Caster type
Understanding different caster types is crucial for your operation. Let me break down each type and explain exactly when and where you should use them.
Swivel Casters
Think of swivel casters as the ultimate multitaskers in your facility. They’re the ones that give you 360-degree rotation capability.
Key Features:
- Full 360° rotation
- Kingpin or kingpinless designs
- Typical height: 1-2″ taller than rigid casters
- Weight capacity: Usually 80-90% of rigid caster capacity
Rigid Casters
These are your straight-line champions. Rigid casters are fixed in position and only roll forward and backward.
Key Features:
- Fixed wheel position
- Simpler construction
- Lower overall height
- Higher load capacity
Locking Casters
Safety first! Locking casters add an extra layer of security to your material handling equipment.
Types of Locks:
1.Total Lock:
- Locks both wheel and swivel
- Maximum security
- Best for sloped surfaces
- Highest cost option
2. Wheel Lock Only:
- Prevents wheel rotation
- More economical
- Still allows swivel
- Good for flat surfaces
3. Swivel Lock:
- Locks swivel mechanism
- Converts to rigid temporarily
- Good for straight runs
- Maintains wheel rotation
Dual-Wheel Casters
When you need extra capacity without extra height, dual-wheel casters are your go-to solution.
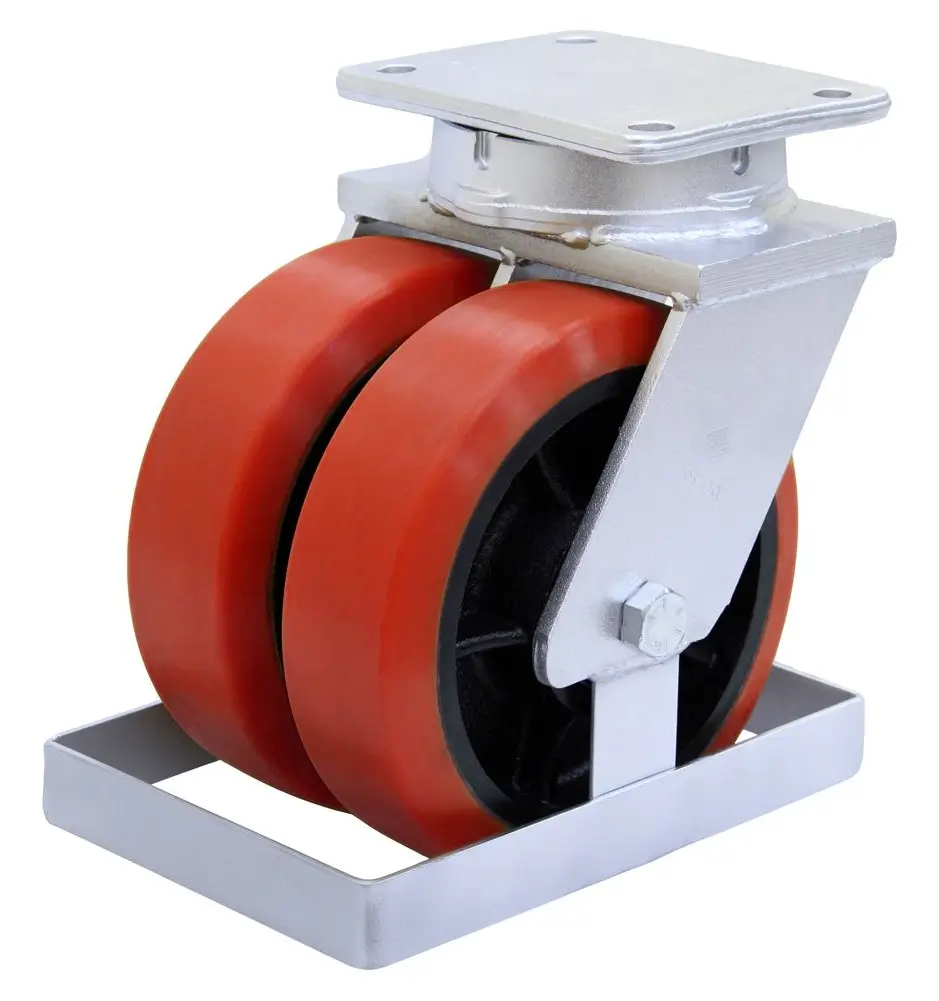

Key Benefits:
- Increased load capacity
- Better weight distribution
- Reduced floor pressure
- Smoother operation
💡 Pro tip: For optimal heavy-duty applications, I often recommend combining different caster types. For example, using rigid casters on one end and swivel casters on the other end of a cart provides both stability and maneuverability.
Step 2: Choosing the Movement Patterns
Straight-line movement only:
- Choose: All rigid casters
- Benefits: Maximum capacity, stability
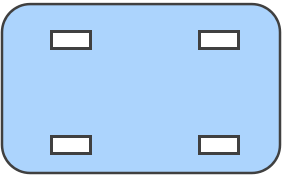
Occasional turning:
- Choose: 2 rigid + 2 swivel
- Benefits: Good compromise of stability and maneuverability
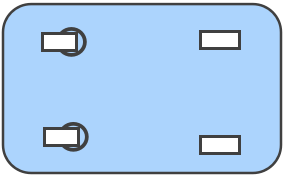
Frequent maneuvering:
- Choose: All swivel casters
- Benefits: Maximum maneuverability
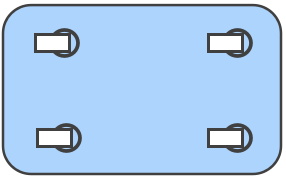
Extra heavy loads:
- Choose: Dual wheel or heavy-duty singles
- Benefits: Increased capacity, better weight distribution
3. Calculate Load Capacity
This is where the rubber meets the road (pun intended). Load capacity isn’t just about picking a caster that can handle your weight – it’s about understanding how that weight impacts your entire operation.
How to Calculate Load Capacity
Here’s the formula I always recommend to my clients:
Required capacity × 1.5 = Recommended minimum capacity per caster
Learn how to calculate caster load capacity and use our caster load capacity calculator to get the job done.
Why multiply by 1.5? Because dynamic loads (when the equipment is moving) can create force spikes up to 50% higher than static loads. Trust me, this safety factor has saved many of my clients from premature caster failure.
Load Limits vs. Maximum Capacity
Here’s something that might surprise you: the maximum capacity rating isn’t necessarily your optimal working load. Consider these factors:
- Shock loads from uneven surfaces
- Weight distribution shifts during movement
- Impact from starting and stopping
- Additional weight from future load increases
💡 Pro tip: For applications with frequent movement or sudden stops, I recommend going even higher – up to 2 times your calculated capacity. It’s better to over-specify than risk equipment failure.
4. Choose Wheel Tread Materials
The right wheel material can make the difference between smooth sailing and constant headaches. Let me break down the main options and when to use each one.
Rubber
Perfect for when you need shock absorption and floor protection. Here’s what you need to know:
- Ideal for: Uneven surfaces, noise reduction, floor protection
- Load capacity: Moderate (up to 1,500 lbs per wheel)
- Best features: Quiet operation, excellent shock absorption
- Limitations: Not suitable for high temperatures or chemical exposure
- Durometer range: 70A-85A (Shore A scale)
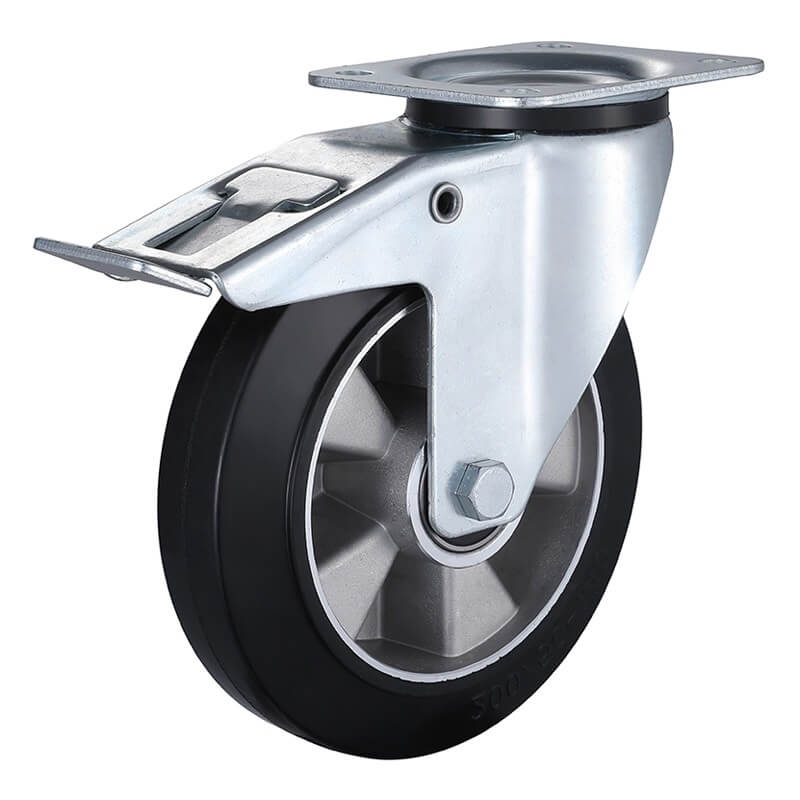

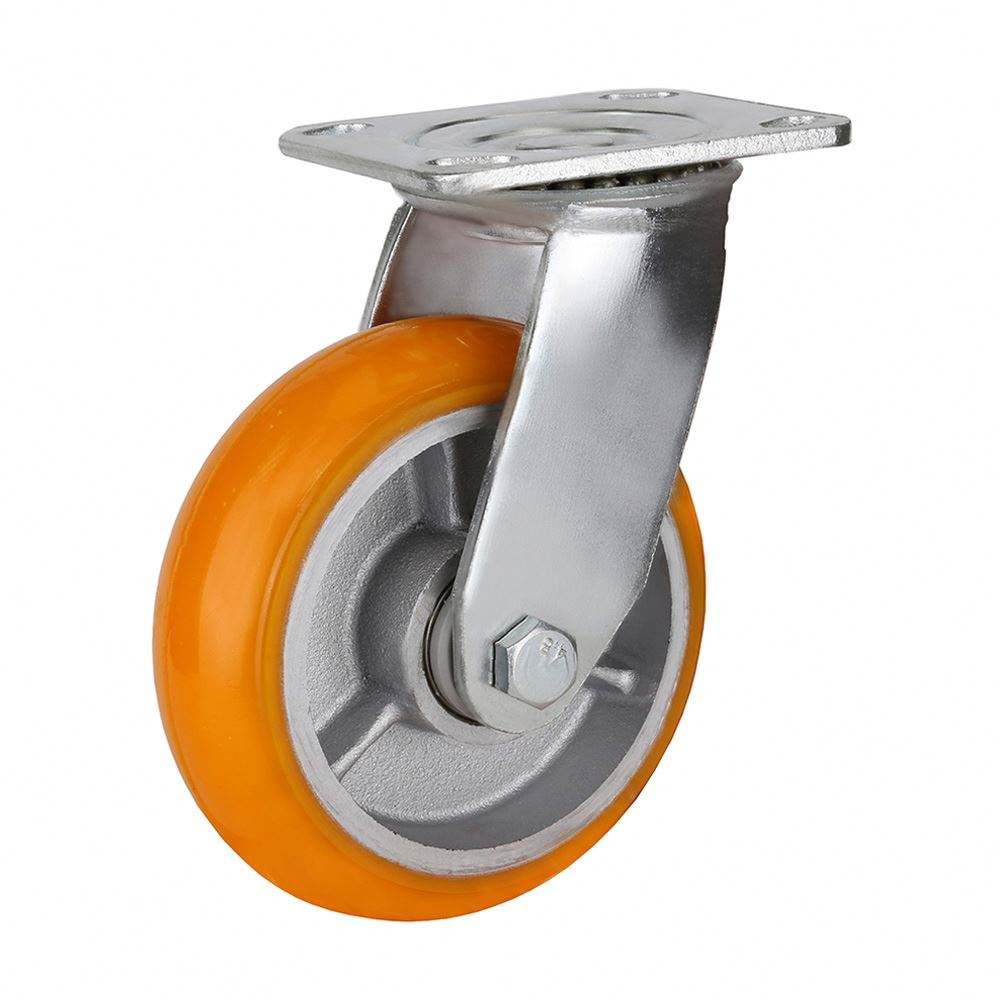
Polyurethane
My go-to recommendation for most industrial applications. Here’s why:
- Ideal for: High-load capacity, frequent use
- Load capacity: High (up to 7,500 lbs per wheel)
- Best features: Excellent wear resistance, low rolling resistance
- Limitations: Limited chemical resistance
- Durometer range: 95A-70D (Shore scales)

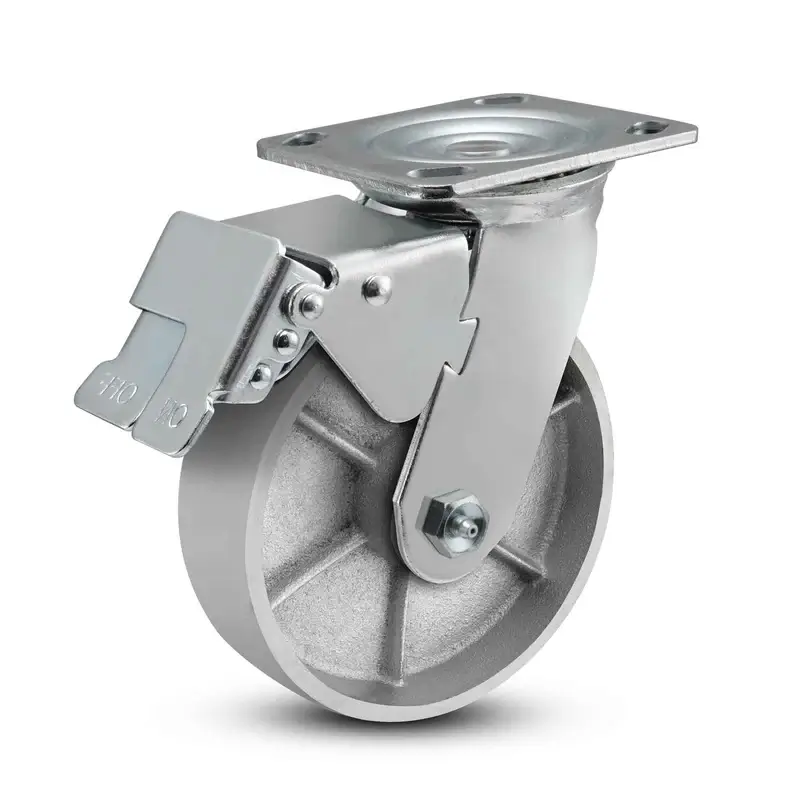
Steel
When durability is your top priority:
- Ideal for: Extreme loads, high-temperature environments
- Load capacity: Very high (20,000+ lbs per wheel)
- Best features: Maximum durability, high-temperature resistance
- Limitations: Can damage floors, noisy operation
- Best used on: Steel plates, extremely rough surfaces

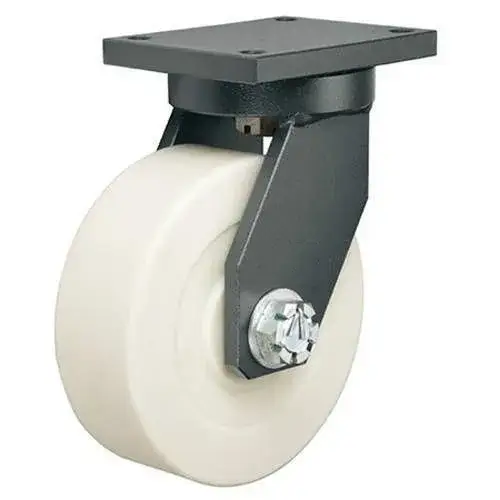
Nylon
The lightweight champion with surprising strength:
- Ideal for: Clean environments, moderate loads
- Load capacity: High (up to 5,000 lbs per wheel)
- Best features: Chemical resistance, non-marking
- Limitations: Limited shock absorption
- Best used in: Food processing, pharmaceutical facilities, heavy manufacturing

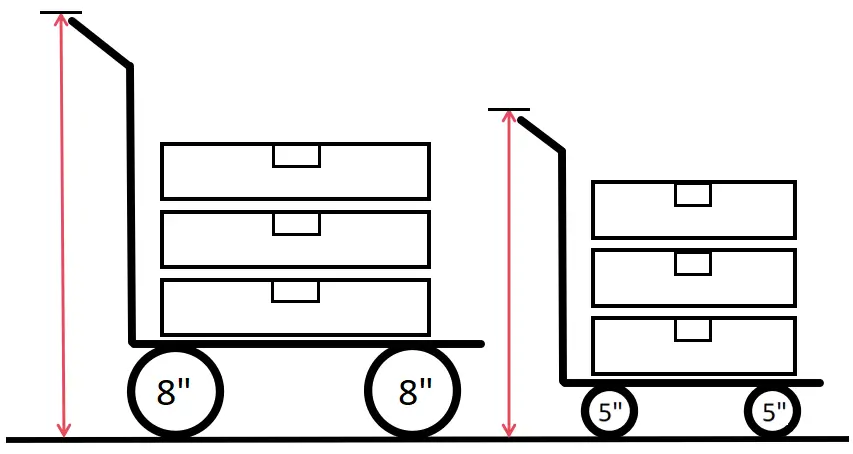
5. Determine Wheel Size and Diameter
Getting the wheel size right is crucial for optimal performance. Think of it like choosing tires for your car – bigger isn’t always better, but too small can make everything harder.
Selecting the Appropriate Diameter
Here’s my rule of thumb for wheel diameter selection:
Larger wheels (8″+ diameter):
- Easier to roll over obstacles and gaps
- Better for uneven surfaces
- Reduced rolling resistance
- Ideal for manual movement of heavy loads
- Lower starting resistance
Smaller wheels (3″-6″ diameter):
- Better for tight spaces
- Lower overall height
- Higher weight capacity per wheel
- More economical
- Better for powered applications
💡 Pro tip: For every 1″ increase in wheel diameter, you typically reduce rolling resistance by about 10%. But remember, larger wheels also mean a higher cart or equipment height.
Comparative Analysis of Heavy-Duty Caster Types
Let’s break down the key differences between various caster types to help you make an informed decision.
Table 1: Caster Type Comparison
| Feature | Rigid Casters | Swivel Casters | Dual-Wheel | Spring-Loaded |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Highest | 80-90% of Rigid | Very High | Medium-High |
| Maneuverability | Straight line only | 360° rotation | Good | Excellent |
| Maintenance Needs | Lowest | Moderate | Higher | Moderate |
| Initial Cost | Lowest | Moderate | Highest | High |
| Best For | Long straight runs | Tight spaces | Heavy loads on sensitive floors | Shock absorption |
| Typical Lifespan | 5-7 years | 3-5 years | 4-6 years | 4-5 years |
Table 2: Wheel Material Comparison
| Material | Load Capacity | Floor Protection | Noise Level | Temperature Range | Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | High (up to 7,500 lbs/3,400KG) | Excellent | Low | -40°F to 180°F (-4℃ to 82℃) | Good |
| Steel | Very High (20,000+ lbs/9,000KG) | Poor | High | -100°F to 500°F (-38℃ to 260℃) | Excellent |
| Rubber | Moderate (1,500 lbs/680KG) | Excellent | Very Low | -20°F to 160°F (-6℃ to 70℃) | Poor |
| Nylon | High (5,000 lbs/2200KG) | Good | Moderate | -40°F to 200°F (-4℃ to 93℃) | Excellent |
Table 3: Application-Specific Recommendations
| Industry | Recommended Type | Wheel Material | Special Features | Maintenance Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Swivel/Rigid Combo | Polyurethane | Toe Guards, Brakes | Weekly |
| Warehousing | All Swivel | Polyurethane/Nylon | Total Lock Brakes | Monthly |
| Clean Room | Stainless Steel | Sealed Precision | Special Seals | Bi-weekly |
| Outdoor/Marine | Rigid | Stainless/Steel | Sealed Bearings | Weekly |
| Heavy Industry | Dual Wheel | Steel/Metal | Shock Absorption | Daily |
Table 4: Cost-Benefit Analysis
| Type | Initial Cost* | Maintenance Cost/Year* | Expected Lifespan | Total Cost of Ownership** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Heavy-Duty | $80-120 | $40-60 | 2-3 years | $200-300 |
| Premium Heavy-Duty | $150-250 | $20-40 | 5-7 years | $250-450 |
| Dual Wheel | $200-300 | $50-70 | 4-6 years | $400-600 |
| Spring-Loaded | $180-280 | $30-50 | 4-5 years | $300-500 |
*Per caster
**Over 5 years, including initial cost
💡 Pro tip: Use these comparison tables as a starting point, but remember that your specific application might have unique requirements that could change these general recommendations.
Table 5: Extreme Environment Specifications
| Environment Type | Recommended Materials | Special Features | Temperature Range | Maintenance Needs | Relative Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Temperature | Steel, Phenolic | Heat Shields | Up to 500°F | Weekly | High |
| Corrosive | 316 Stainless Steel | Sealed Bearings | -40°F to 180°F | Bi-weekly | Very High |
| Freezer/Cold | Special Polyurethane | Sealed Bearings | Down to -40°F | Monthly | High |
| Washdown Areas | Stainless Steel | Sealed Swivel | Up to 180°F | Weekly | High |
| Chemical Processing | Chemical-Resistant Poly | Protection Boots | 0°F to 180°F | Weekly | Very High |
These comparative tables should help you make a more informed decision based on your specific needs and operating environment. Remember to consider all factors – not just initial cost or load capacity – when making your final selection.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies
Let’s look at some real-world scenarios to understand how proper caster selection and implementation can transform operations. These examples will help you visualize how the principles we’ve discussed apply in practice.
Enhancing Efficiency in Manufacturing
Problem:
A large manufacturing facility was experiencing frequent downtime due to failing casters on their heavy material transport carts. Their existing setup:
- Load weight: 3,000 lbs per cart
- Usage: 16 hours per day
- Environment: Concrete floors with occasional debris
- Previous solution: Standard industrial casters
Solution Implemented:
- Upgraded to heavy-duty polyurethane wheels
- Installed kingpinless swivel casters
- Added precision bearings
- Implemented scheduled maintenance program
Results:
- 75% reduction in caster-related downtime
- Extended caster life from 6 months to 2 years
- Decreased push force required by 40%
- Significant reduction in floor damage
Key Takeaways:
- Proper capacity matching is crucial
- Quality matters in high-use scenarios
- Preventive maintenance pays off
- Worker ergonomics impact productivity
Optimizing Warehouse Mobility
Challenge:
A distribution center needed to improve their order picking efficiency while handling varying load weights. Their situation:
- Variable loads: 500-2,500 lbs
- Multiple floor types
- Frequent direction changes
- Limited maintenance resources
Solution Design:
- Implemented hybrid caster configuration
- Swivel casters with total locks front
- Rigid casters rear
- Added ergonomic handles
- Selected dual-durometer wheels
- Installed spring-loaded casters
Impact:
- 30% increase in picking speed
- Reduced worker fatigue reports by 60%
- Minimal maintenance requirements
- Improved maneuverability in tight spaces
Improving Outdoor Equipment Durability
Scenario:
A shipyard needed reliable caster solutions for outdoor equipment storage and movement. Their challenges:
- Harsh marine environment
- Heavy loads (5,000+ lbs)
- Exposed to elements
- Rough concrete and metal surfaces
Implementation:
- Stainless steel construction
- Sealed precision bearings
- Special marine-grade wheels
- Enhanced braking systems
Outcomes:
- Extended service life in corrosive environment
- Reduced maintenance frequency
- Improved safety in wet conditions
- Better mobility on rough surfaces
💡 Pro tip: While these case studies show impressive results, remember that each application is unique. Use these examples as inspiration but always analyze your specific needs when designing your solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s address the most common questions I receive about heavy-duty casters. I’ve chosen these questions based on real conversations with clients, focusing on the issues that matter most to industrial applications.
Q: How do I determine the load capacity needed for my casters?
A:
The formula is straightforward but crucial:
Calculate total weight (equipment + maximum load)
Add 15-30% for dynamic forces
Divide by number of casters
Multiply by safety factor (1.5-2.0)
Example: For a 2,000 lb load on a 500 lb cart:
Total static weight: 2,500 lbs
Add 20% for dynamics: 3,000 lbs
Divided by 4 casters: 750 lbs each
With 1.5 safety factor: 1,125 lbs minimum per caster
Q: What materials are best for outdoor applications?
A:
For outdoor use, consider these factors:
Stainless steel components for corrosion resistance
UV-resistant wheel materials
Sealed precision bearings
Weather-protective covers or boots
Best material choices:
Wet conditions: Polyurethane or rubber wheels
Rough surfaces: Solid steel or high-impact nylon
Corrosive environments: 316 stainless steel components
High UV exposure: Special UV-resistant compounds
Q: Are swivel casters better than rigid casters for maneuverability?
A: It depends on your application:
Swivel Casters Excel At:
Tight spaces
Frequent direction changes
Complex maneuvering
Manual operation
Rigid Casters Are Better For:
Straight-line movement
Higher speeds
Heavier loads
Towed applications
Best Practice: Consider a combination – rigid casters on one end and swivel on the other for optimal control and capacity.
Q: How do environmental factors affect casters?
A: Environmental factors significantly impact caster performance and durability.
High temperatures can soften wheel materials like rubber and polyurethane, while extreme cold may cause them to become brittle.
Moisture exposure leads to rust in standard steel components, requiring stainless steel options in wet environments.
UV radiation from sunlight can degrade wheel materials, especially in outdoor applications.
Floor debris and chemical exposure also affect caster longevity, making material selection crucial for specific environments.
In coastal or high-humidity locations, choosing corrosion-resistant materials is essential for optimal performance.
Q: What safety features should I look for in heavy-duty casters?
You should consider braking systems, physical protection like toe guards, and well calculated load ratings.
In wheelswaycaster.com, we’ve set up a caster load capacity calculating tool, feel free to use it!
How often should I maintain my caster wheels?
Maintenance frequency depends on usage.
Daily use, full check monthly.
Moderate Use: full check quarterly.
Light use: full check semi-annually.
Conclusion
Selecting the right heavy-duty casters is crucial for your operation’s efficiency and safety. By carefully considering the caster type, load capacity, wheel material, and size requirements we’ve discussed, you can make an informed decision that matches your specific needs. Remember, a well-chosen caster system is an investment in your equipment’s performance and your team’s productivity. If you need additional guidance, don’t hesitate to consult with a professional caster supplier who can help fine-tune your selection. 👉 eric@wheelswaycaster.com






